When you switch to an electric vehicle (EV), one of the first questions you’ll likely have is, “How long does it take to charge?” Understanding the charging time is essential for planning your day, whether you’re commuting, running errands, or planning an awesome weekend at the Falls. So what’s the answer?
The truth is that the time it takes to charge an EV can vary widely based on several factors, including the type of charger, the size of your battery, and your vehicle’s charging capacity. This guide will break down everything you need to know about EV charging times, so you can ensure that you’re on the road when you need to be.
The Different Types of EV Chargers Explained

The time it takes to charge your EV primarily depends on the type of charger you’re using. There are three main types of chargers, each with its own speed.
Level 1 Chargers (120-Volt)
A Level 1 charger is the most basic option, typically plugging into a standard household outlet. These chargers are usually included with the purchase of your EV. They add about 3-5 miles of range per hour of charging. If you drive a car with a 250-mile range, this means that it could take up to 50 hours to charge from empty to full. While this seems long, Level 1 chargers can be perfectly fine if you drive short distances daily and charge overnight.
Level 2 Chargers (240-Volt)
Level 2 chargers, which are much faster, are commonly found at public charging stations and workplaces. They can also be installed in your home. They require a 240-volt outlet, similar to what your dryer or oven uses.
In terms of charging speed, these chargers can add 15-30 miles of range per hour, meaning a full charge can take anywhere from 4 to 10 hours, depending on your vehicle’s battery size. For many EV owners, installing a Level 2 charger at home is a game-changer, allowing them to charge their car overnight or during the workday.
DC Fast Chargers (Level 3)
DC Fast Chargers are the quickest way to charge an EV and are typically found at public charging stations along highways and in commercial areas. They convert AC power to DC power, which can be delivered directly to the battery at a much faster rate.
Depending on the charger and the vehicle, a DC Fast Charger can bring an EV from 10% to 80% in as little as 20 to 40 minutes. However, these chargers are usually more expensive to use than Level 1 or Level 2 chargers.
Factors Affecting Charging Time
While the type of charger is a significant factor in determining charging time, several other elements can also impact how quickly your EV charges:
- Battery Size: Larger batteries take longer to charge. For example, a vehicle with a 100 kWh battery will take longer to charge than one with a 50 kWh battery, even if you’re using the same charger. However, larger batteries typically provide more range, so you may not need to charge as frequently.
- State of Charge (SOC): The charging time can also depend on your battery’s current state of charge. Charging from 20% to 80% is usually faster than charging from 0% to 100%. Many EVs, and chargers themselves, reduce the charging speed as the battery gets closer to full to protect the battery and ensure longevity.
- Charging Speed of Your Vehicle: Not all EVs can accept the same charging speeds. Even if you’re using a fast charger, your vehicle’s onboard charger might limit the rate at which it can charge. This is why some cars take longer to charge than others, even on the same type of charger.
- Environmental Factors: Temperature can affect charging times. Batteries charge more slowly in cold weather, which can be a consideration during the winter months in cities like Hamilton. Some EVs have battery preconditioning features that warm up the battery before charging to ensure optimal charging speed.
- Charging Habits: How often you charge and how low you let your battery get before plugging in can also influence your charging times. Regularly topping up your battery, rather than waiting until it’s nearly empty, can reduce the time you spend charging.
Charging at Home vs. Public Charging
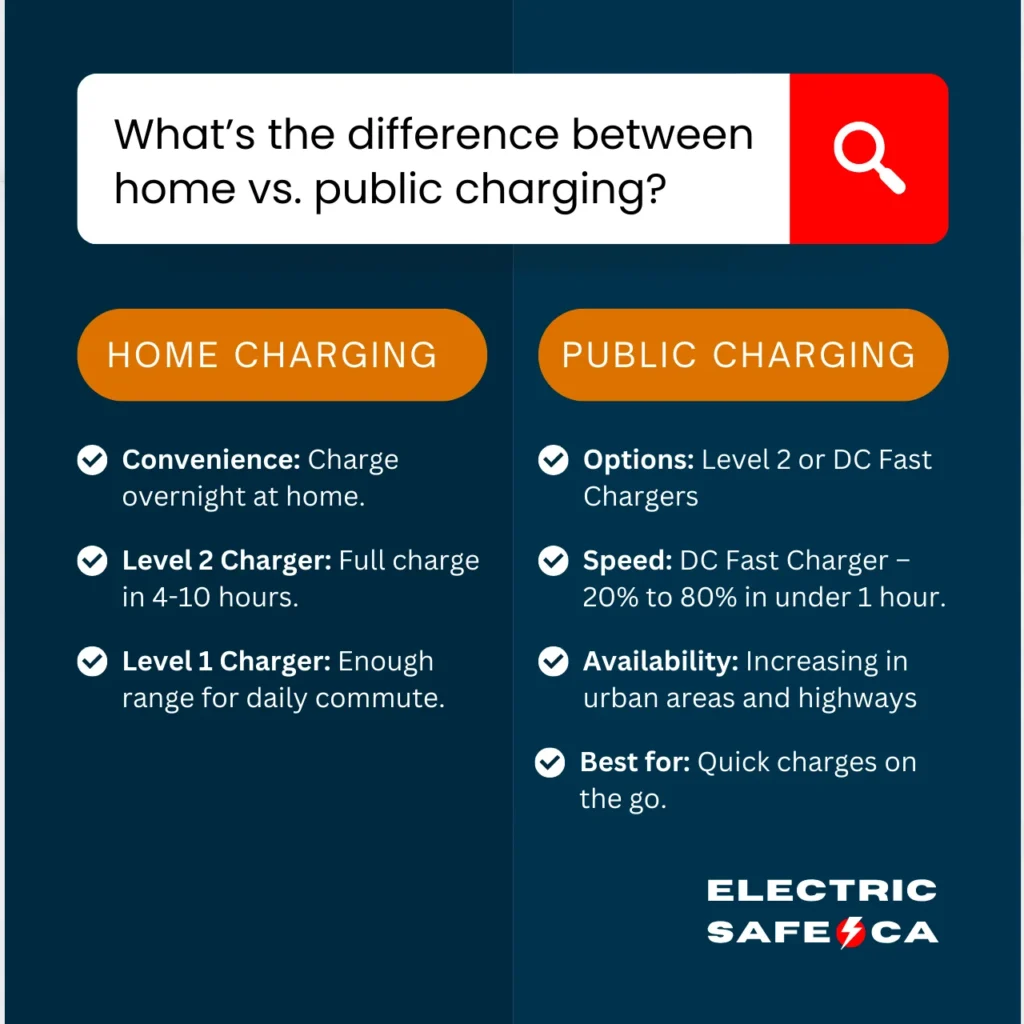
When considering how long it will take to charge your EV, it’s important to think about where you’re charging—at home or at a public station.
Home Charging
Having an EV charger installed at home is all about convenience. With a Level 2 charger installed at home, you can plug in your vehicle overnight and wake up to a full battery every morning. Even if you’re using a Level 1 charger, you can still gain enough range overnight for your daily commute. A Level 2 charger can fully charge most EVs within 4 to 10 hours.
Public Charging
Public charging stations often provide Level 2 or DC Fast Chargers. These are great when you’re on the go and need a quick charge. DC Fast Chargers can significantly reduce charging time, bringing your battery from 20% to 80% in under an hour. The availability of public charging stations can vary, but they’re becoming more common, especially in urban areas and along major highways. Planning your trips around available charging stations can minimize the time you spend waiting for your EV to charge.
Real-World Charging Scenarios
Let’s look at a few typical scenarios to give you a better idea of how long charging might take.
Daily Commuter
Suppose you have a Nissan Leaf with a 40 kWh battery and a Level 2 charger at home. You drive 30 miles a day, and your EV gets about 150 miles of range on a full charge. If you plug in each night, replenishing the battery fully would take about 2-3 hours.
Weekend Road Trip
Now imagine that you have a Tesla Model 3 Long Range with a 75 kWh battery. You’re taking a road trip and need to top up your battery after driving 200 miles. Stopping at a DC Fast Charger, you can add about 150 miles of range in 20-30 minutes, enough to continue your trip.
Running Errands
You’re out running errands in your Chevrolet Bolt EV (66 kWh battery) and decide to plug in at a public station while you shop for an hour. Using a Public Level 2 charger, you can add about 25 miles of range in an hour, enough for your drive home and more.
Interested in the associated costs? Take a look at our other article for insights into the cost of EV charging in Hamilton, Ontario.
How to Optimize Your Charging Time
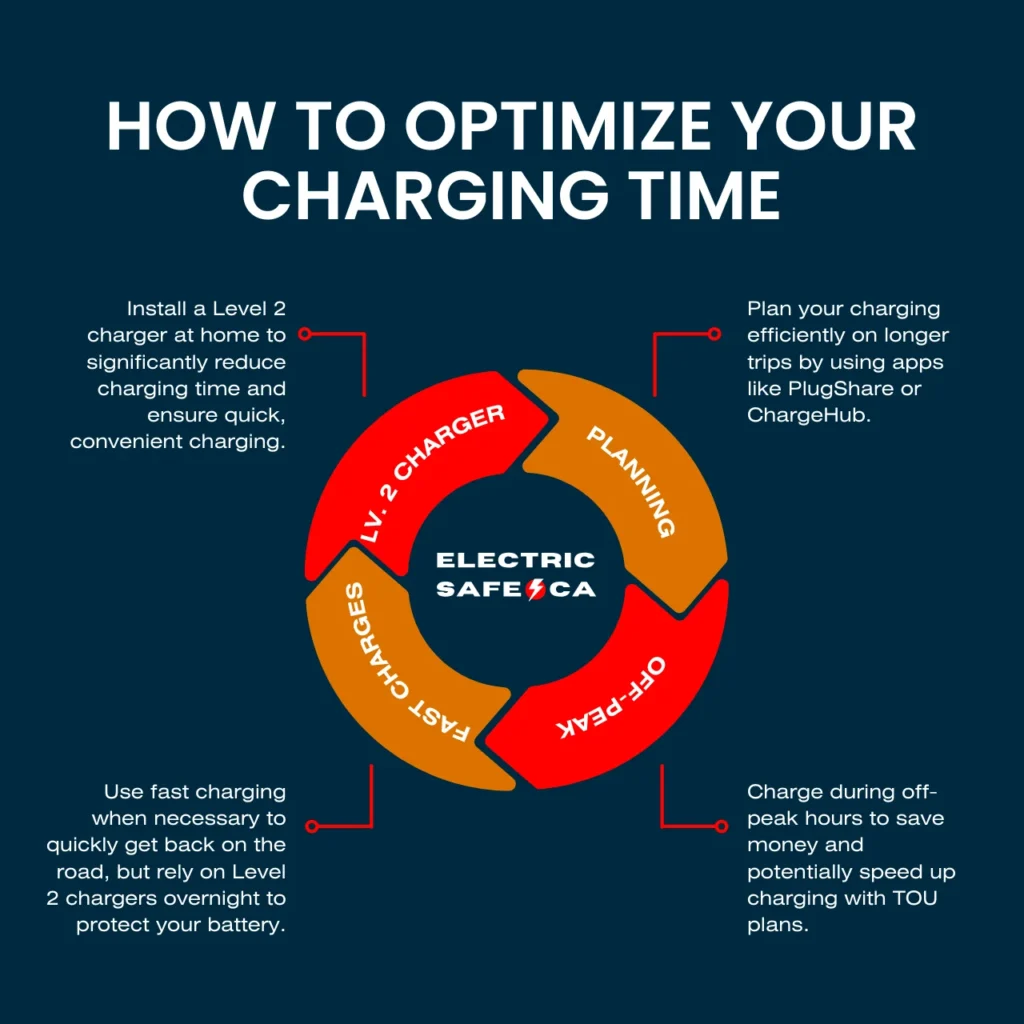
Here are some tips to help you make the most of your charging time:
- Install a Level 2 Charger at Home: If you can, install a Level 2 charger at home. This will drastically reduce your charging time compared to using a standard household outlet and will give you the flexibility to charge your EV quickly when needed.
- Plan Your Charging: When using public chargers, especially on longer trips, plan your route ahead of time to include charging stops. Apps like PlugShare or ChargeHub can help you find available stations and even check if they’re currently in use.
- Charge During Off-Peak Hours: If you’re using a TOU electricity plan, charging during off-peak hours can save you money and might even result in faster charging if the grid is less congested.
- Take Advantage of Fast Charging When Necessary: Use DC Fast Chargers when you need to get back on the road quickly but rely on slower Level 2 chargers for regular, overnight charging to preserve your battery’s health.
Charge Your EV More Efficiently
Understanding how long it takes to charge your EV is key to managing your time and making the most out of your electric vehicle. Whether you’re charging at home, at work, or on the road, knowing the variables that affect charging time can help you plan properly and ensure that your EV is always ready when you need it.
If you’re considering installing a home charging station or need any electrical work to support your EV, contact ElectricSafe. Our EV charger electricians can help set up a safe and reliable charging solution tailored to your needs. To schedule a free quote, call (647) 559-9382.




